Patrick Meinzinger, KUKA: “New generation robots can bring OEMs significant reductions in CO2 emissions and energy consumption”
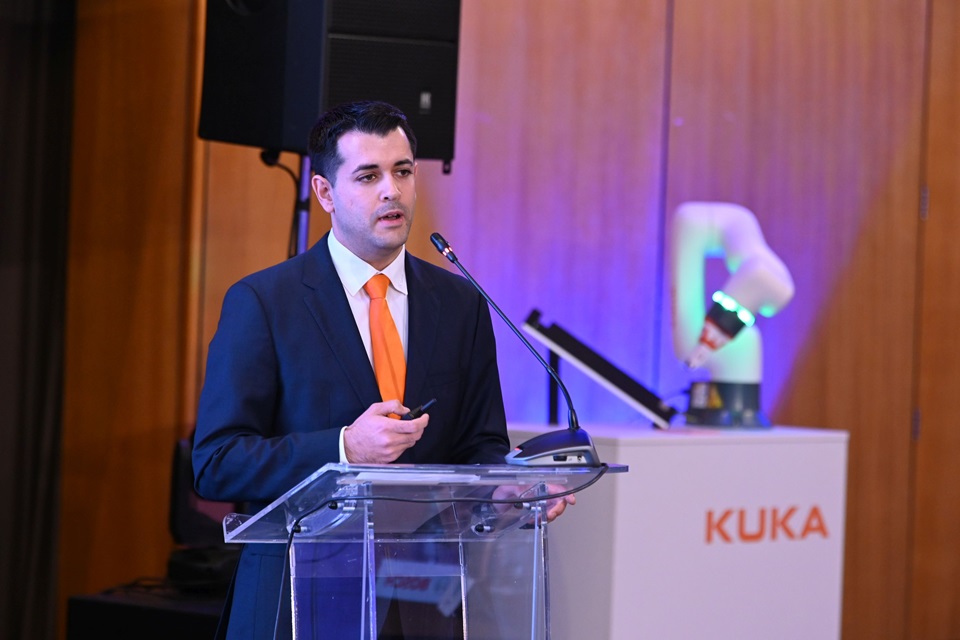

“What is the lifecycle of a robot in the automotive industry? Normally, automotive manufacturers use the robots for seven years. Then they have a model change, or a facelift and the robots run for another seven years. So, in total we are talking about 14 years of usage. Some companies use the robots for 21 years, but 14 years is the normal lifecycle for robots used by OEMs worldwide,” Patrick Meinzinger, Business Development Manager – Automotive, KUKA said during Automotive 2023 Forum organized by Automotive Today and The Diplomat-Bucharest.
“The potential for cost reduction by reducing energy consumption is enormous. Over the last 20 years, we developed our technology to be more energy efficient. We have achieved approximately 60 percent reduction in energy consumption in the last 12 years.
New generation robots can bring you up to approximately 1.3 million Euro reduced CO2 costs and 7.2 million Euro reduced energy costs (calculation with 500 robots over 14 years of use).
There are a number of factors which are influencing energy consumption: payload, speed, temperature, path planning, robot positioning.
We have implemented the DC network in Germany, which brings enormous potential for energy savings and grid stability.
How to make your business more energy efficient? “Think energy” already in the planning phase; pick the right robot for the right task; consider energy efficiency in simulation and commissioning; adapt infrastructure to modern 650 DC supply; track energy CO2 footprint over time to identify deviations.”
Full recording of the conference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9P1kYtDifKc